How Does Texas’ Third-Party Rooftop Solar Permitting Law Work?

SB1202 gives homeowners a powerful new tool to bypass long delays from local authorities, making it easier to get clean, resilient home power. By Ian SeamansCity Hall AdvocateEnvironment Texas Research & Policy Center The adoption of solar energy in Texas is getting a major boost! Thanks to Senate Bill 1202, which passed in the 89th Texas […]
Solar Energy Technologies Office | Resources for Consumers

These resources, compiled by the U.S. Department of Energy Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO), cover a wide variety of topics, from the process of choosing and installing a solar energy system, to understanding how it impacts the value of a home. Learn more below. Learn how to save on solar and review federal solar tax credit resources. […]
Solar financial incentives for property owners (2024-2032)
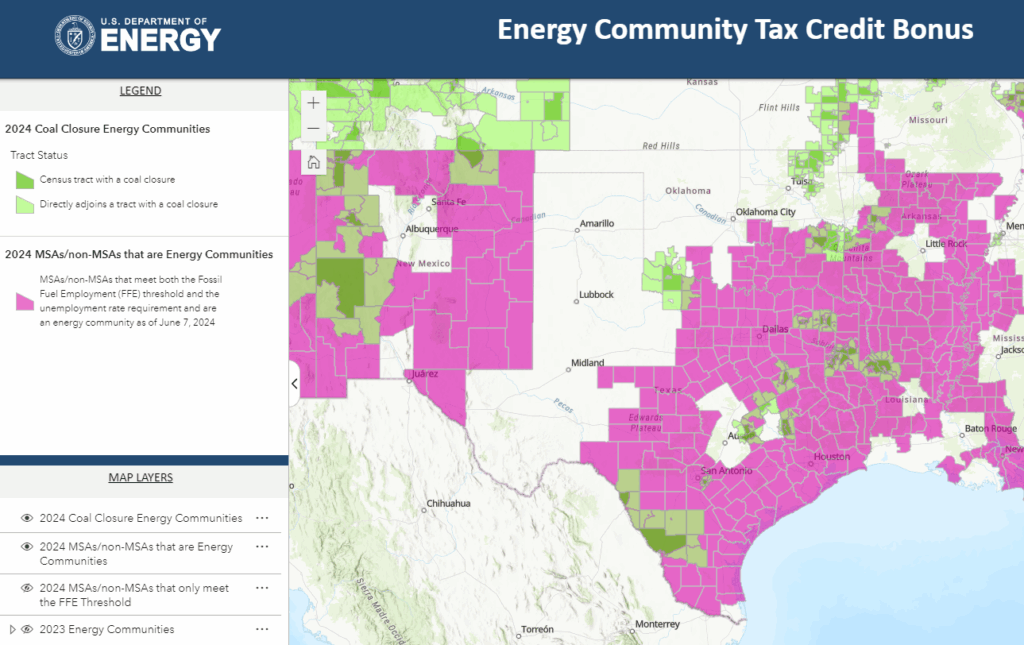
This is a summary of publicly available resources as compiled by Solvari Solar. Property owners should refer to the resources linked in this document for the status of any incentives mentioned. This summary does not represent tax or financial guidance in any form. Talk to your certified licensed financial experts for more details on how […]
Heat Pumps Vs Solar Hot Water Systems

Should you install a solar hot water or heat pump hot water system for your home? This article from Energy Matters Australia takes a look at the pros and cons of each to help you decide. Solar hot water systems have been around for almost as long as solar PV systems have been gracing our rooftops. Heat […]
Solar + Storage vs. Generators in the United States
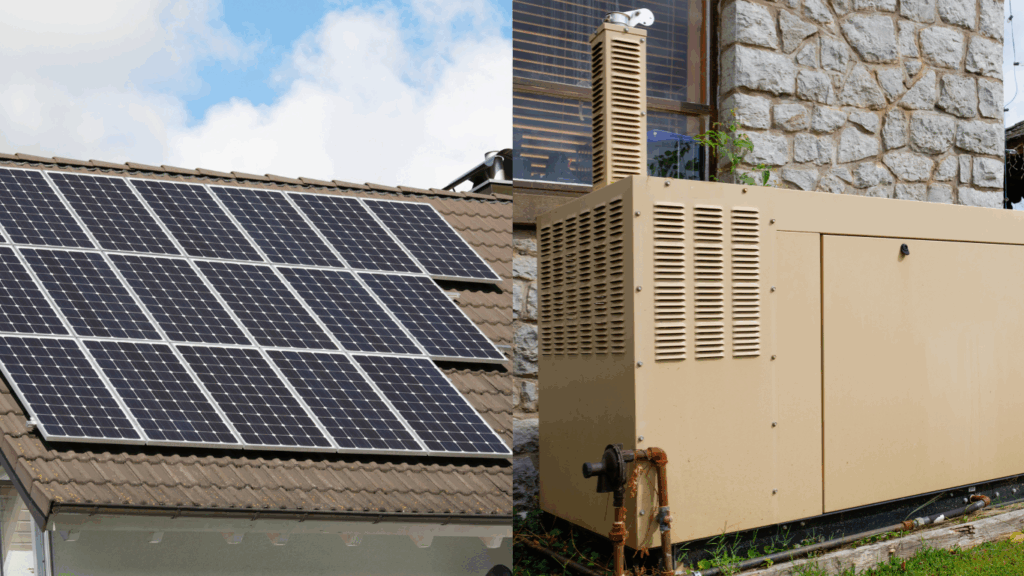

By Mohammad Alkhatib In the United States, the need for reliable backup power solutions is increasing due to frequent power outages and natural disasters. Solar storage systems and traditional generators are two prominent options for ensuring continuous power supply during outages. This report provides a comprehensive comparison of these two solutions, analyzing their pros and […]
New Value of Solar Study: Rooftop Solar Cuts Costs for the Texas Grid

TXSES commissioned a new study quantifying grid-stabilizing value and cost savings of rooftop solar For Immediate Release: July 16, 2024Contact: José Medina, jmedina@citizen.org AUSTIN, Texas—Energy supplied by rooftop solar is much more valuable than the average kilowatt-hour sent to the ERCOT grid by other means, finds a new study commissioned by the Texas Solar Energy […]
New Pathways for Equitable Solar Adoption in Texas

As part of the Solar Energy Innovation Network (SEIN) Round 3 program, a diverse group of energy stakeholders in Texas set out to develop and pilot new pathways to increase rooftop solar adoption to low income households. The vision: deploy rooftop solar to households owned or rented by low-income families at no cost by pairing […]
Solar Maintenance: Roof Repairs
While some distributed solar systems can be ground-mounted or placed atop car ports, the vast majority of residential systems are placed atop a homeowner’s roof. As such, it’s helpful to know what changes, if any, need to be made to a roof before installation, and for replacement and upkeep down the road. Additional resources:● U.S. […]
Winter Storm Uri: Impacts on Low-Income Texans

Almost every Texan remembers Winter Storm Uri, which in 2021 highlighted the inadequacies of the ERCOT power grid as it faced total failure. However, the consequences were not uniform. Read the report to learn more about how low-income Texans were disproportionately burdened by the storm and subsequent ERCOT failings. Download the full report.
